Nanoparticle colloids
are mixtures in which metal nanoparticle's are dispersed in a liquid medium. The particles of a colloid remain dispersed and do not settle due to gravity, and they are often electrically charged.
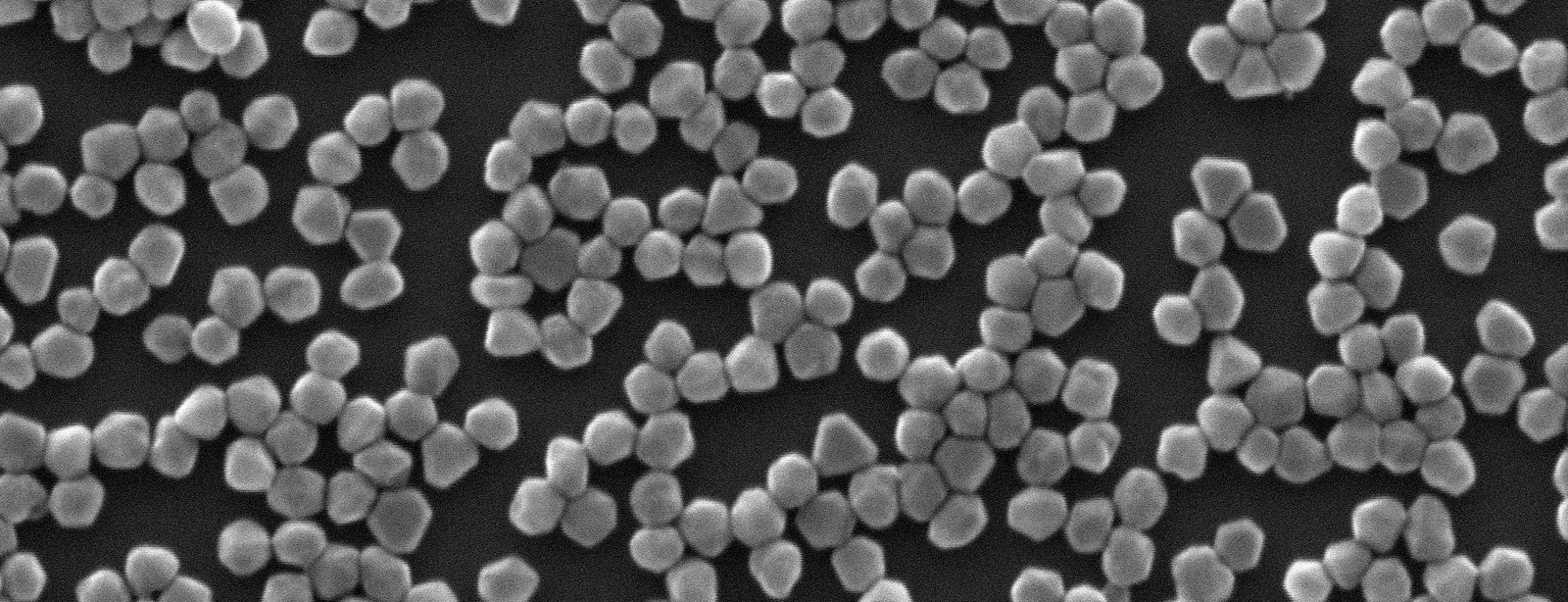
are mixtures in which metal nanoparticle's are dispersed in a liquid medium. The particles of a colloid remain dispersed and do not settle due to gravity, and they are often electrically charged.
Product and Application
|
We produce semi-monodispersed metal nanoparticles in a wide range of their size and shape by wet chemical synthesis and femtosecond laser ablation in liquids.
catalysts, etc. |
Advantages
Large surface area |
Expressed catalytic properties |
High light absorption in the visible spectrum |
Good biocompatibility after surface functionalization |
Synthesis technology
| Technics | Material | Size | Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical synthesis | Silver | 20 - 200 nm | 4 - 23% |
| Physicochemical synthesis (femtosecond laser irradiation of metallic targets situated in pure water) | Gold, silver, copper | 80 - 160 nm | 34 - 36% |
*Depending on the application, nanoparticles can be dispersed in different solvents or deposited on solid or flexible substrates.
| Our nanoparticles primarily are prepared as one of the consumables for templated deposition or for your own needs. |
References
A. Šileikaitė, J. Puišo, I. Prosyčevas, S. Tamulevičius. Investigation of Silver Nanoparticles Formation Kinetics During Reduction of Silver Nitrate with Sodium Citrate // Materials Science-Medziagotyra 15 (1) 21-27, 2009 https://matsc.ktu.lt/index.php/MatSc/article/view/26114/13296
D. Peckus, A. Tamulevičienė, K. Mougin, A. Spangenberg, L. Vidal, Q. Bauerlin, M. Keller, J. Henzie, L. Puodžiukynas, T. Tamulevičius, S. Tamulevičius. Shape influence on the ultrafast plasmonic properties of gold nanoparticles // Optics Express 30 (15) 27730-27745, 2022 https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.463961
N. Khinevich, D. Peckus, A. Tamulevičienė, G. Klimaitė, J. Henzie, T. Tamulevičius, S. Tamulevičius. Size and crystallinity effect on the ultrafast optical response of chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles // Journal of Materiomics, 17 September 2023 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2023.08.009